Grade Levels By Age
In the United States, students are typically grouped into different grade levels based on their age. These grade levels help organize and structure the education system. Here’s a general breakdown of grade levels by age:
Preschool: Ages 3-5
Preschool is usually for children between the ages of 3 and 5. It’s a place for young kids to begin their early education in a playful and interactive environment.
Kindergarten: Age 5-6
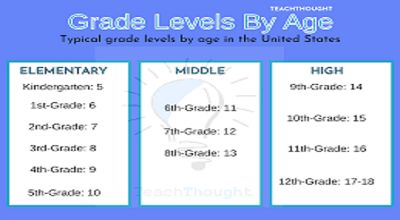
Kindergarten is the first formal grade in school, usually for children aged 5 to 6. It focuses on basic skills like reading, writing, and math in a fun and supportive setting.
Elementary School
- 1st Grade: Age 6-7
- 2nd Grade: Age 7-8
- 3rd Grade: Age 8-9
- 4th Grade: Age 9-10
- 5th Grade: Age 10-11
Elementary school encompasses grades 1 through 5. Students learn fundamental subjects like English, math, science, and social studies.
Middle School or Junior High School
- 6th Grade: Age 11-12
- 7th Grade: Age 12-13
- 8th Grade: Age 13-14
Middle school or junior high school includes grades 6 through 8. It’s a transitional period where students begin to explore more subjects in-depth.
High School
- 9th Grade (Freshman): Age 14-15
- 10th Grade (Sophomore): Age 15-16
- 11th Grade (Junior): Age 16-17
- 12th Grade (Senior): Age 17-18
High school comprises grades 9 through 12. It’s a critical phase where students prepare for college or their future careers.
College or University
After high school, many students choose to attend college or university, where they pursue higher education and specialize in specific fields.
Exceptions and Variations
While the age-grade level breakdown I provided earlier is a general guideline, there can be exceptions and variations based on individual circumstances, regional differences, and educational systems. Here are some exceptions and variations to consider:
Early or Late Starters
Some children may start school a year earlier or later than the typical age due to developmental readiness or other factors. This flexibility is common in preschool and kindergarten.
Grade Skipping
Gifted or academically advanced students may skip a grade to match their abilities and interests. For example, a student might move from 1st grade directly to 3rd grade.
Homeschooling
Homeschooled students may not follow the traditional age-grade structure. They can progress at their own pace and grade levels may not align with standard ages.
International Differences
Grade levels and ages can vary between countries. In some nations, the school starting age and grade structure differ from those in the United States.
Special Education
Students with special needs may be placed in different grade levels or receive customized educational plans to meet their unique requirements.
Alternative Education
Some schools and educational programs, like Montessori or Waldorf schools, have different grade structures and philosophies that deviate from the conventional model.
Individual Progress
Some students may progress more quickly or slowly in certain subjects, leading to variations in grade levels within the same school year.
Transition Periods
Transition points, such as moving from elementary to middle school or from middle school to high school, can vary in different regions and educational systems.
Summary
In summary, you can note that these age ranges can vary slightly depending on the country and the education system. But this general guide should give you a clear idea of grade levels by age in the United States.
It’s important to consult with local schools or educational authorities to understand specific age-grade requirements and any potential exceptions or variations in your area. Education is a dynamic process, and the goal is to provide the best learning experience for each student, taking into account their individual needs and circumstances.